Nikada
preamble
Recently, I have written a few articles titled “Sell While You Can.” If you follow Deere & Company (Germany) may remember article I predicted that a stock price drop was imminent. NVIDIA (Nasdaq:NVDA) (Neoe:NVDA:CA) AI Small Fish InvestmentWhile the article inspires optimism about Nvidia’s future AI dominance, it also portends tough times for the company across the Western world and in markets outside of China.
If you follow chip news, you’re well aware that the U.S. government has been imposing sanctions on China with the same fervor as Wall Street bankers selling mortgage-backed securities to Greece. For example, last October, Reported The US government has tightened export controls on Nvidia’s cutting-edge AI chips. These chips are The move escalated a technology war that has seen China denounce the restrictions. The United States implemented similar restrictions the previous year to prevent China from acquiring powerful AI technologies.
A year has passed, Restrictions are not workingApparently, despite the US ban on the sale of advanced AI chips to China, various institutions are still acquiring them through unknown resellers. Experts who have looked into the matter in detail claim that the chips were likely diverted without the manufacturers’ knowledge. The US is now investigating potential violations, and Nvidia has said it will take action if necessary. The server maker claims that it complied with regulations and that the products it sold were not cutting-edge.
As you might expect, not only was the ban only partially effective, but it also prompted domestic Chinese companies like Huawei to develop alternatives to Nvidia.
As an Nvidia investor, I’m hopeful the company can navigate the challenges of selling to China, but I’m not convinced Tesla (NASDAQ:TSLA) have been unable to sustain revenues and profit margins.
Tesla is caught up in it A brutal price war In China, Tesla has been forced to cut prices on several models to maintain sales amid growing competition from established automakers and newer EV makers such as BYD and Xiaomi.
These aggressive price cuts are coming at the expense of Tesla’s profits, which are shrinking at an alarming rate in China, where domestic manufacturers such as BYD offer cars that are significantly cheaper, about a third cheaper than Tesla’s lowest-priced model.
I used to Intel and Am In the Chinese market
Nvidia’s Finances
Overall, Last Quarterly Report We paint a picture of a thriving company that is well positioned in AI technology and can expect long-term growth.
Driven by its data center division, sales surged 262% year-over-year, and the company’s AI-related business is expected to continue experiencing remarkable growth in the future.
In fact, it was hard to find any downsides. The report highlighted the company’s growing profitability due to high operating leverage and a shift towards higher-margin products such as the Blackwell suite. And given the growth in all things AI-related, investors are surely looking forward to more above-expected earnings going forward.
Let’s not forget the announcement of a 10-for-1 stock split, which will push the stock price in a direction that investors will be happy with.
Now, let’s address the potential obstacles to success in China. Addressing the challenges in the Chinese market due to export restrictions, the company has a strategy to overcome the hurdles set by the US government. In fact, the company suggested that more competition from Chinese companies would stimulate further innovation for Nvidia.
Nvidia’s latest Filing of Form 10-KChina accounts for about 17% of Nvidia’s total revenue, while “other countries” also account for about 17%. These “other countries” include Western countries and countries outside of Western influence, such as Indonesia and Russia.
NVIDIA Sales by Region (Nvidia Form 10K)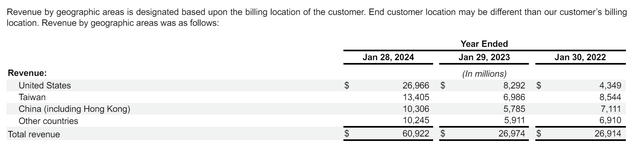
in recent years, U.S. Export Restrictions Nvidia is restricting the types of chips it can sell in China. As we all know, cutting-edge AI chips are banned. But now Specially designed for the Chinese market As a result of the restrictions, it has been placed on the banned list.
To deal with this, NVIDIA has had to develop improved, lower performance versions of its chips to comply with U.S. export regulations. Simply put, NVIDIA is forced to sell products with specifications far below its cutting edge technology.
To say the situation is fluid would be an understatement: U.S. regulations and enforcement actions are continually changing, all of which could affect the chips Nvidia is able to sell in China.
Huawei
Back in 2023, Reported U.S. export restrictions on advanced AI chips to China could create unexpected opportunities for Huawei and its Ascend chips.
Analysts said Huawei’s Ascend chips are roughly on par with Nvidia’s Chinese chips in terms of raw power, but still behind in performance. But the report goes on to argue that Huawei has had challenges developing a software ecosystem built around Nvidia’s CUDA platform, which allows for the training of complex AI models, something Huawei’s CANN alternative struggled with at the time. Tech experts estimated it would take 5-10 years for Huawei to catch up, but Huawei produced a competitive product much sooner than expected.
Latest Report
NVIDIA’s Initiatives China’s AI chip market The launch of the H20 chip has been a struggle. Despite being the company’s most powerful chip designed specifically for China, the H20 has gotten off to a weak start. There appears to be an oversupply in the market, forcing Nvidia to slash prices and sell the H20 for less than Huawei’s competing Ascend 910B chip.
Additionally, Huawei is expected to ramp up production of its Ascend 910B chip this year, which could outperform the H20 in several key areas.
Huawei’s emergence as a formidable competitor should understandably be a major concern for investors.
According to Reuters, analysts are increasingly concerned about Nvidia’s long-term prospects in the Chinese market, which contributes a large part of the company’s revenue. And the price war is just one example of the fierce competition Nvidia faces in China. China’s push to develop domestic chips and government mandates to prioritize Chinese-made chips are creating further headaches for Nvidia.
Although several large Chinese tech companies have placed orders for the H20, overall demand appears to be weak. Government procurement data suggests interest in the H20 is weaker than Huawei’s products. To make matters worse, the need to undercut Huawei, combined with the rising manufacturing costs of the H20, is putting pressure on Nvidia’s profit margins.
About a million H20 chips are expected to ship to China over the next few months, and Nvidia’s success will reportedly depend on whether it can effectively compete with Huawei on price and performance. But if you ask me, if Nvidia struggles to sell the H20 for less than the Ascend 910B, that bodes very badly.
Manufacturing
Huawei has acquired SMIC, China’s largest semiconductor foundry.OTCQX:SIUIF), producing new advanced chips.
SMIC reportedly plans to forego cutting-edge extreme ultraviolet (EUV) equipment and rely on older equipment to manufacture Huawei-designed chips. Deep UV (DUV) technology. Self-aligned quadruple patterningor SAQP, reduces reliance on high-end lithography.
whether Huawei and SMIC It remains to be seen whether SAQP can be used to achieve mass production of advanced chips. The research and development effort is seen as a key step in China achieving self-sufficiency in chip manufacturing.
If mass production of advanced chips becomes a reality, I think there will be satisfactory markets outside of China.
Potential market
It’s pretty much a secret that Huawei is not well-received across the Western world, but the company can sell its products in BRICS+ countries and non-aligned countries like Indonesia, so its Ascend series could soon compete with Nvidia outside of China, especially in Russia.
Potential customers for Huawei include Chinese data center giant GDS Holdings Limited.global) is making major inroads into Southeast Asia. Joint Ventures The company is working with Indonesia’s sovereign wealth fund to develop a comprehensive data center platform across Indonesia, with an initial focus on building a large hyperscale data center campus on the island of Batam.
The facility boasts a net floor area of 10,000 square metres and an IT power capacity of 28 MW. GDS sees this collaboration as a validation of its expertise and a stepping stone for further expansion within Indonesia.
Another potential buyer for Huawei chips is Tencent Holdings.OTCPK:TCEHY) is a well-known Chinese cloud company. The company was founded in 2012. facility It has a data center in Jakarta that is now fully operational. Besides Indonesia, Tencent has data centers in the United States, Singapore, Russia, Germany, Canada and India. article Explains Tencent’s expansion into MENA.
risk
As I said, this article offers an alternative to the consistently positive narrative we see so often in the media, and I will be the first to admit that there are risks to this less-than-enthusiastic bullishness: First, while non-Western countries may want the best, at the moment there is no one that can match Nvidia’s offerings.
Second, even if they lose some business in China, which seems highly likely, their revenue growth outside of China is likely to be quite impressive.
summary
U.S. restrictions have clearly thwarted Nvidia’s plans to sell its most advanced AI chips in China, forcing the company to push lower-spec versions. To complicate matters further, Huawei has emerged as a formidable competitor.
Huawei’s Ascend chips are gaining popularity and may outperform Nvidia’s H20 in the Chinese market. Of course, lower demand and lower prices for the H20 could hurt Nvidia’s profits.
And there is always the possibility that at some stage Huawei could gain a foothold in other countries through a company specialising in Chinese data centres.
Additionally, Huawei is expected to ramp up production of its Ascend 910B chip this year, which could outperform the H20 in several key areas.
Huawei’s emergence as a formidable competitor should understandably be a major concern for investors.
According to Reuters, analysts are increasingly concerned about Nvidia’s long-term prospects in the Chinese market, which contributes a large part of the company’s revenue. And the price war is just one example of the fierce competition Nvidia faces in China. China’s push to develop domestic chips and government mandates to prioritize Chinese-made chips are creating further headaches for Nvidia.
Additionally, Huawei is expected to ramp up production of its Ascend 910B chip this year, which could outperform the H20 in several key areas.
Huawei’s emergence as a formidable competitor should understandably be a major concern for investors.
According to Reuters, analysts are increasingly concerned about Nvidia’s long-term prospects in the Chinese market, which contributes a large part of the company’s revenue. And the price war is just one example of the fierce competition Nvidia faces in China. China’s push to develop domestic chips and government mandates to prioritize Chinese-made chips are creating further headaches for Nvidia.




