Cyber is an expanding net new growth area with opportunities to offer attractive insurance products, especially to the mid-market. However, the path to becoming a market-leading and profitable cyber insurance company is fraught with challenges. This article outlines key strategies for developing top-tier cyber products, culminating in a guide to seven strategic cyber steps for chief underwriting officers.
Why midmarket cyber has unique challenges to mitigate
The cyber risk landscape is rapidly evolving, so insurers can, for example, enable data-driven continuous learning from past claims, provide a seamless quoting and binding process, and avoid unintended We need a robust framework to reduce risk aggregation.
The small business market typically purchases standard cyber coverage in person or online, while the midmarket market consists of businesses that receive services from brokers and agents. These companies are looking to insurers for both basic and advanced capabilities to effectively address the unique challenges of midmarket cyber risk. Key challenges specific to cyber in the mid-market include:
Transparency and clarity for brokers and agents: As the mid-market is primarily served by brokers and agents, it is important that insurers’ risk appetite and underwriting approaches are transparent. Does the insurance company offer a dedicated cyberbroker portal? leverages its existing portal across multiple lines of business, but the key is to have transparent risk appetite and make it seamless for brokers to compare quotes and place trades. Additionally, it is essential to provide an accurate quote on the same day.
Both standard and custom policies required: The middle market consists of companies that purchase both standard and custom insurance. Therefore, insurers must be able to quickly respond to changes in policy terms, exclusions, or different combinations of higher deductibles or limits. Some midsize businesses have advanced requirements regarding risk mitigation, prevention, and incident response planning. For large mid-market customers, detailed exposure analysis may be required to design appropriate insurance coverage.
Large amount of data: Standard cyber policy (name, industry, revenue, customer website) requires no more than 4 data points for small business customers, but much more for mid-market customers is. While some data points can be obtained through open APIs or structured data ingestion from brokers, the more complex the risk, the more likely the relevant data points will arrive in unstructured documents.
Establishing a robust digital infrastructure for cyber insurance
Cyber insurance companies require fundamental functionality across sales, quoting, and binding to ensure seamless business processes. The operating model begins and ends with a focus on customer and broker experience. Whether the insurer chooses to organize according to customer segments (e.g. middle market) center This was done in the CC department (for example, a dedicated one-stop-shop cyber team across distribution, underwriting and claims), or depending on the business area (e.g. a dedicated one-stop-shop cyber team across distribution, underwriting and claims). It is important that it is a conscious choice. level.
All customers, whether or not they purchase cyber insurance, should quantify their cyber risks and define key cyber risk scenarios as part of their incident response plans. Failure to do so will expose you to unknown and potentially significant risks to your entire balance sheet. Some insurers may choose to invest in risk scenario capabilities, while others may rely on brokers or outsource to cybersecurity experts. The capabilities required for detailed exposure analysis include some insurers offering pre-incident advice and training, cyber stress testing, cybersecurity readiness validation tools, detection and response solutions, and safe spaces for incidents. Similar to what we offer in Cyber Safe Room. Response planning, notification services, and built-in claims services.
The important basic functions of cyber are: powerful digital core Achieve master data management according to your goals. Insurers need strategic tools such as a robust digital core and fit-for-purpose master data management to perform detailed exposure analysis at the quote stage. These tools facilitate the accumulation of granular risks and aggregate them based on various parameters such as industry sector, underlying hardware and software, cybersecurity maturity, supply chain, jurisdiction, and company size. Establish a framework for measuring and understanding your cyber risk exposure. A detailed exposure management framework is essential to effectively mitigate the risk of unintended risk aggregation.
Building market-leading advanced cyber capabilities
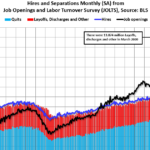
A key element to becoming a market-leading cyber insurer is that technology and data capabilities must be designed to work at scale and in real-time. Cyber insurance is one of the most challenging areas due to the potentially catastrophic and borderless nature of breaches. Cyber incidents, like oil spills, can be evolving and unpredictable and can have a significant impact on businesses, society, and critical infrastructure such as hospitals, water and wastewater systems, and airports. Today, the potential for insurers to face unintended risk aggregation is a clear and immediate threat.
As previously mentioned, mid-market cyber policies require capturing and modeling more data points during the quote and bind stages. Additionally, at the time of first notification of a loss, there can be hundreds of relevant data points, far more than, say, for an auto insurance claim, and insurers typically have 20 vehicle-specific data points. ~30 data points (vehicle details, intended use, witness details, IoT data, etc.). For cyber claims, there are over 100 data points that can be relevant for continuous learning and improvement. These include exposure management, actuarial tables, and risk management in underwriting systems. This allows market-leading insurers to maintain profitability through a robust risk appetite and pricing framework.
as Previously Despite this coverage, there is a shortage of cyber talent who are proficient in cybersecurity protocols and have a deep understanding of constantly evolving regulations and laws across IT, AI, GDPR, and consumer privacy. While investing in talent and continually improving the skills of underwriters and claims adjusters, there are high-impact use cases for cyber insurance for AI and Gen AI solutions. We’ve seen AI and Gen AI save insurance companies dozens of hours a month, freeing them up to focus on: Niche and dangerous risk areas that require deep human expertise.
Insurers with a strong digital core can move quickly to accelerate profitable growth in cyber, but most insurers are slow to implement AI and Gen AI at scale. We are becoming aware of the investment required. per AccenturePulse of Change Research46% of insurance executives say it will take more than six months to scale up Gen AI technology and realize its potential benefits. If your applications and data aren’t in the cloud and don’t have a strong security layer, it’s virtually impossible to reap the benefits of Gen AI at scale.
7 Strategic Cyber Steps for Chief Underwriting Officers
In today’s rapidly evolving technology environment, chief underwriting officers face the critical task of navigating their organizations through the complexities of cyber insurance. The following strategic steps are a roadmap for insurance companies to not only survive, but thrive in this challenging environment.
- Define your identity in cyber insurance. Decide whether you want to be a conservative insurer, a hasty follower, or a market leader. This choice will guide your investments and emphasize cyber as a core part of your business.
- establish Your cyber brand: Determine your company’s distinctive offerings in cyber insurance, including cutting-edge risk consulting, competitive pricing, AI-powered streamlined processes, and a strong reputation for claims services.
- Select your specialty: Choose to establish a dedicated mid-market center of excellence (CoE), a cyber-specific CoE, or a hybrid operating model.
- Improved responsiveness: Convert or introduce new features and provide accurate quotes within hours.
- Improving underwriting: Determine the optimal number of underwriting variables for technical pricing. Reverse engineer the process to capture critical data during the broker submission and claim notification stages.
- Evaluate cyber exposure management. Engage external experts to assess your cyber exposure controls to avoid unintended risk aggregation.
- Invest in people: Focus on talent strategies that strengthen skills and integrate advanced technologies such as AI and Gen AI to address the evolving cyber risk landscape.
Measure your path to becoming a cyber market leader
Designing and implementing a major cyber insurance framework presents significant challenges. Key aspects include defining success, establishing metrics, and determining the actions needed to achieve these goals. Continuous monitoring of financial and operational metrics is essential to make timely adjustments and ensure profitable growth in the cyber midmarket. Please contact us for further discussion. Carmina Leeds and Matthew Madsen.