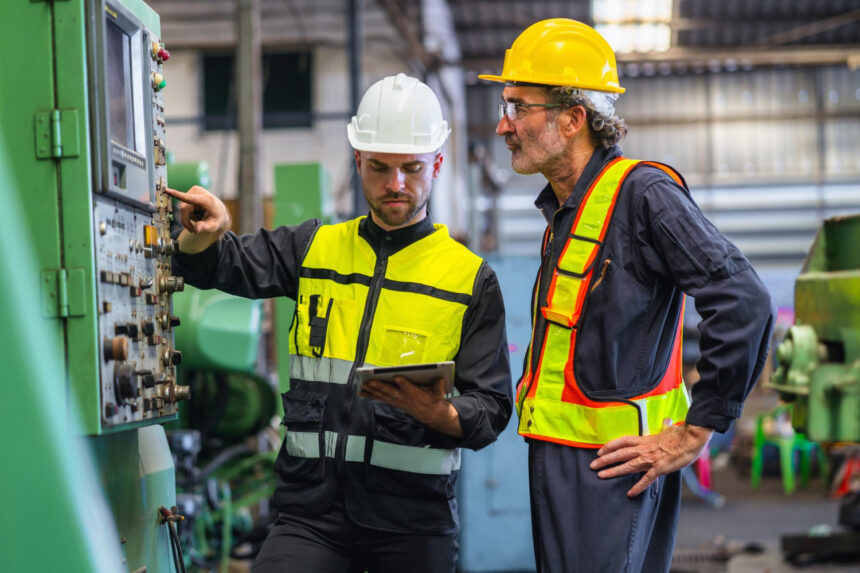
Predictive maintenance uses data to improve the performance of manufacturing equipment. This involves collecting information from sensors within the machine, analyzing this data to detect problems, and using predictive models to predict potential problems.
In contrast to traditional maintenance methods, which often rely on scheduled repairs or fixes as problems occur, PdM continuously monitors the condition of equipment and predicts failures before they occur. This approach helps improve efficiency and extend the life of industrial assets.
Why predictive maintenance is necessary in manufacturing operations
Traditionally, the industry has relied on two primary maintenance approaches: reactive and preventive. Corrective maintenance refers to repairing equipment after it has failed, while preventive maintenance refers to scheduled checks to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Reactive maintenance can lead to unplanned downtime and expensive repairs, especially for older machines. Preventive maintenance can help reduce downtime, but often results in unnecessary costs for equipment that is in good condition.
Predictive maintenance provides a better approach by using data to track equipment performance and condition in real time. By analyzing this data, companies can identify potential problems, predict when equipment will fail, and plan maintenance accordingly. This data-driven approach eliminates guesswork and allows you to do more. Efficient maintenance planning.
How to implement predictive maintenance in manufacturing
1. Analyze current data
Before diving into predictive maintenance, understand your current situation. Carefully review past downtime incidents and note their frequency and impact. Identify and classify equipment defects and calculate associated costs. Finally, assess past maintenance efforts, distinguishing between reactive and preventive actions for each asset.
2. Identifying priority assets
Use insights to identify which assets are most critical to your business. Next, attach condition monitoring devices and IoT sensors to these key pieces of equipment. You don’t have to use every device available. A good approach is to start with the essentials, such as a thermal imaging camera, vibrometer, and oil measurement tool.
3. Start a pilot project
Instead of jumping into large and expensive predictive maintenance (PdM) projects, start small. Start a pilot project using one or two of your most important assets and machines to test and refine your approach.
4. Make detailed plans in advance
It’s important to have a clear vision of your goals. Create a detailed implementation plan with a realistic budget and schedule. Define your PdM project goals, make them measurable, and regularly track progress to ensure successful outcomes.
Benefits of predictive maintenance in manufacturing
1. Achieve better ROI
Predictive maintenance (PdM) provides significant return on investment (ROI). PdM reduces maintenance costs by avoiding unnecessary routine maintenance tasks. PdM also reduces both unplanned and planned downtime. Data scientists know exactly where the problem is, making remediation faster. Additionally, manufacturers can order replacement parts and new machinery in advance, reducing delays and saving on inventory costs.
2. Extend machine life
According to Deloitte research, PdM increases machine uptime by up to 20%. This system monitors equipment performance and detects problems before they cause significant damage. As a result, the lifespan of the machine is extended because it runs until its end of life, rather than having to be replaced periodically as in preventive maintenance.
3. Improve operator safety
Early warning of equipment problems can help prevent manufacturing injuries. By analyzing big data and monitoring machines, predictive maintenance can identify safety risks and unsafe conditions, making your workplace safer.
4. waste reduction
Manufacturers can help You can profit by reducing waste. As equipment begins to wear out, waste often increases in areas such as materials, energy, machine usage, and worker time. PdM can detect these problems before they become serious.
5. Improved performance
Predictive maintenance reduces both repair time and frequency. Over time, this increases the efficiency of manufacturing operations, improves plant conditions, and reduces equipment breakdowns.
6. protect your assets
While repairing equipment, there is a risk of affecting other parts of the equipment. Predictive maintenance (PdM) helps identify abnormal behavior after repairs, allowing you to address issues early and protect your assets.
Examples of using predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is essential for manufacturers looking to keep their operations running smoothly and avoid costly downtime. Here are some common uses of predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
1. Optimize equipment life
By continuously monitoring equipment condition, predictive maintenance can help extend the life of expensive machinery. For example, car factories use it to track the status of robotic arms to prevent unexpected breakdowns and maximize productivity.
2. Reduced maintenance costs
Predictive maintenance helps reduce costs by eliminating the need for routine maintenance activities. For example, chemical processing plants use predictive maintenance to schedule maintenance Reduce unnecessary service costs and allocate resources where they are needed most, based on actual equipment conditions.
3. Improved safety
Identifying potential equipment failures before they occur helps create a safer work environment. In the oil and gas industry, monitoring drilling rigs for signs of wear can prevent accidents and protect workers.
4. Improving product quality
Maintaining equipment in top condition leads to improved product quality. Pharmaceutical manufacturers can use predictive maintenance to meet rigorous industry standards and ensure consistent, high-quality production.
Examples of predictive maintenance in the manufacturing industry
1. general motors
General Motors (GM) has introduced predictive maintenance (PdM) that uses IoT sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor assembly line robots. The system helps GM detect early signs of equipment wear, preventing unexpected breakdowns and extending machine life. For example, at GM’s Saginaw metal casting operations, this approach reduced unplanned downtime by 15% and saved approximately $20 million in annual maintenance costs. Production efficiency and safety have also improved.
2. Mondi
Mondi, a paper and packaging products company, uses predictive maintenance to avoid unexpected shutdowns of its Munich factory’s plastic extrusion machines. A single breakdown can cost up to €50,000 to clean and result in lost revenue. By implementing PdM, Mondi was able to save between €50,000 and €80,000, primarily through lower operational costs and reduced waste.
lastly
Predictive maintenance is more than just a trend. It is a practical solution to improve manufacturing efficiency, safety and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging data to predict equipment problems before they occur, manufacturers can minimize downtime, extend machine life, and improve overall performance. While implementing predictive maintenance may require some initial effort, the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile investment for any business. forward-Thinking manufacturing operations.
Author bio:
Lindsay Walker is a Marketing Manager at Sacramento-based NEXGEN, an industry leader in designing advanced computerized maintenance management systems and asset management software tools for the utilities, facilities, utilities, manufacturing, and vehicle industries. In her free time, Lindsay enjoys traveling and reading, which gives her new perspectives and inspiration for her work. She is committed to creating content that successfully connects with readers and enhances their digital experience.