Hi, I’m Yves. If you even casually follow the news about climate change, you’ve probably heard about feedback loops such as melting permafrost releasing methane and increasing carbon levels. In this article, we’ll discuss some local examples of how human activity is affecting the weather on a measurable scale at a national level.
By Kyle Hilburn, atmospheric science researcher at Colorado State University. conversation
Forest fire explosionfire whirls, giant thunderstorms: when a fire gets big enough and hot enough, it can actually create its own weather.
Among these Extreme Fire ConditionsThe usual methods of firefighters fighting fires directly don’t work, and wildfires get out of control. Firefighters mitigate many of these risks. Huge park fire In the summer of 2024, a fire breaks out near Chico, California.
But how does fire create weather?

I Atmospheric Scientist Using data collected by satellites Weather Forecast Model To better predict extreme fire weather events. Satellite data shows that fire-induced thunderstorms are happening more frequently than anyone would have thought possible just a few years ago. Here’s what’s happening.
The relationship between wildfires and weather
Imagine a wilderness with dry grass, shrubs, and trees. A lightning strike or a tree branch hitting a power line creates a spark. If the weather is hot, dry, and windy, that spark can quickly start a wildfire.
When plants burn, they give off a lot of heat. This heats the air near the ground, causing it to rise like a hot air balloon because hot air is less dense than cold air. The cold air then flows in to fill the void left by the rising air.
like this Wildfires create unique wind patterns.
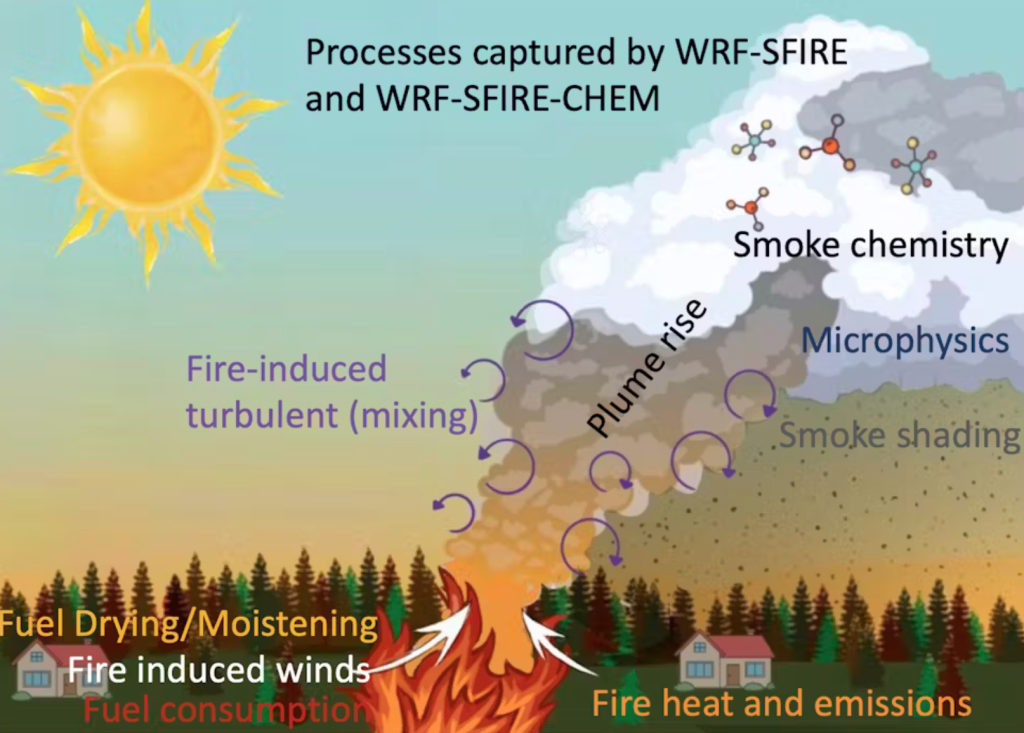
What happens next? Atmospheric stabilityBecause air temperature falls rapidly with height above the ground, the rising air is always warmer than its surroundings and continues to rise. When it rises high enough, moisture condenses, Forming clouds called pyrocumulus Or flammagenitus.
As the air continues to rise, at some point the condensed moisture will freeze.
When liquid and frozen water particles mix in a cloud, Collisions between these particles may lead to Charge SeparationIf the charge buildup is large enough, a discharge (better known as lightning) occurs to neutralize the charge.
Whether the clouds caused by the fire will develop into thunderstorms is Three key elements: Causes of lift, instability and dampness.
Dry Lightening
Wildfire environments are typically moisture-limited. Dry lower atmospheric conditions result in the following: Dry Thunder.
No one who lives in a wildfire-prone environment wants to see dry lightning. Dry lightning occurs when a thunderstorm produces lightning, but the precipitation evaporates before it reaches the ground, meaning there’s no rain to help put out the fires started by the lightning.
Fire Whirlpool
When air rises into the atmosphere, the wind speed and direction can change. This is called ” Wind shearThis causes the air to rotate. The updraft tilts the rotation vertically, Similar to a tornado.
These fire tornadoes can be accompanied by powerful winds that can spread burning ash and start new fire areas, but are not usually true tornadoes because they are not accompanied by rotating thunderstorms.
The waning storm
Eventually, the thunderstorms caused by the wildfires will begin to subside and what rose will subside. The downdrafts from the decaying thunderstorms The winds on the ground are irregularcausing the fire to spread in directions that are harder to predict.
When fires create their own weather, their behavior becomes more unpredictable and erratic, which only increases the threat to residents and firefighters battling the fires. Predicting changes in fire behavior is critical to everyone’s safety.
Satellite images show fire weather events aren’t all that uncommon
Meteorologists are The ability of fires to cause thunderstorms It appeared in the late 1990s, GOES-R series In 2017, scientists High-resolution images It’s important to understand that fire-induced weather is actually common.
Today, these satellites can warn firefighters of new blazes. Before you even call 911That’s important. Increasing tendency The number, size, and frequency of wildfires across the United States.
Climate change and rising fire risks
The risk of heat waves and droughts Increased in North America As global warming progresses, dry land and forests are becoming more flammable. Climate model experiments show that: The risks will continue to increase due to human-induced climate change..
As global warming progresses, more people move to areas at risk of fire. Fire hazard And it is spreading. Chain of Dangers Things that remain long after the fire has died down, such as burnt landscapes The risk of landslides is much higher Such as debris flows that could affect water quality and ecosystems.
It is important to remember that fire is a natural part of the Earth system, and communities can reduce fire. Vulnerability to fire damage Build defensible spaces and firebreaks; Reducing the vulnerability of homes and propertyFirefighters can also reduce surrounding fuel loads through planned fires.
As a fire scientist Stephen J. Pyne Humanity will have to re-establish its relationship with fire and learn to live alongside it, he writes.








