In recent years, startup founders in India have increasingly turned to venture debt (VD) as a strategic funding tool.
This funding approach has gained traction, particularly in sectors such as fintech, where founders prioritize maintaining ownership while accessing essential growth capital, said the Singapore-based asset. According to a new report from Lighthouse Canton, an investment agency specializing in management.
The report is released The paper, published in November titled ‘Silent Bloom: The Rising Influence of VD’, explores the growing adoption of VD in the Indian startup ecosystem.
VD is a strategic finance tool for startups and early-stage companies that are typically backed by venture capital (VC). It often acts as a complement to equity financing and is designed to provide working capital and capital for growth without diluting ownership as significantly as equity financing.
In India, the VD market has been steadily growing, reflecting the early days of VC. The fintech sector, in particular, is emerging as a major adopter of VD, allowing startups to more effectively manage cash flow, support future financing, and drive growth.
According to an industry survey conducted for this report, 67% of Indian fintech founders prefer VD to compete with bank financing, and 80% have VD accounting for more than 11% of the debt capital raised. states. The main reasons for this priority include reduced dilution of existing shareholders (86%), access to capital (57%), and flexibility in repayment schedules and capital utilization.
Fintech leads the VD market
While fintech companies across all industries can benefit from the general benefits of VD, financial companies are currently the biggest adopters of this lending tool in India.
One prominent use case is the forward lending model. In these models, banks lend money to intermediaries such as fintech companies and non-bank financial companies (NBFCs), which then lend money to underserved sectors such as agriculture, small businesses, and affordable housing. provide financing.
In this scenario, VD would provide fintech companies with the liquidity they need to manage their forward financing operations, allowing them to efficiently access these priority sectors while preserving cash flow.
Another use of VD is First Loan Default Guarantee (FLDG) financing. FLDG is a risk-sharing arrangement that guarantees fintech companies cover a small amount of loan defaults in co-financing partnerships with banks. Essentially, the fintech startup deposits money with the bank and acts as a safety net to absorb the default of the initial borrower.
VD is often used to finance these FLDG deposits, allowing fintech startups to participate in such partnerships without using their own equity or cash reserves.
Lighthouse Canton highlights Rupeek and LoanTap, two of its portfolio companies operating in the lending space, as examples of startups benefiting from VD. Rupeek, which specializes in gold loans, leverages VD to expand its financial runway and support growth in loan balances.
Similarly, LoanTap, which focuses on micro, small and medium enterprise (MSME) lending, is not only leveraging VD to expand its lending operations, but also strengthening its technology stack and pursuing strategic acquisitions.
In addition to lending to fintech startups, VD is also used by fintech companies in areas such as payments and embedded finance. Payment gateways utilize VD to bridge the cash flow gap between when a payment is processed and when a settlement is made. This ensures liquidity and supports trading growth.
Embedded finance startups employ VD to fund technology development and expansion, such as application programming interfaces (APIs) and platform integration. This allows you to expand business-to-business (B2B) partnerships and generate stable revenue from financial services fees.
India’s rapidly growing VD market
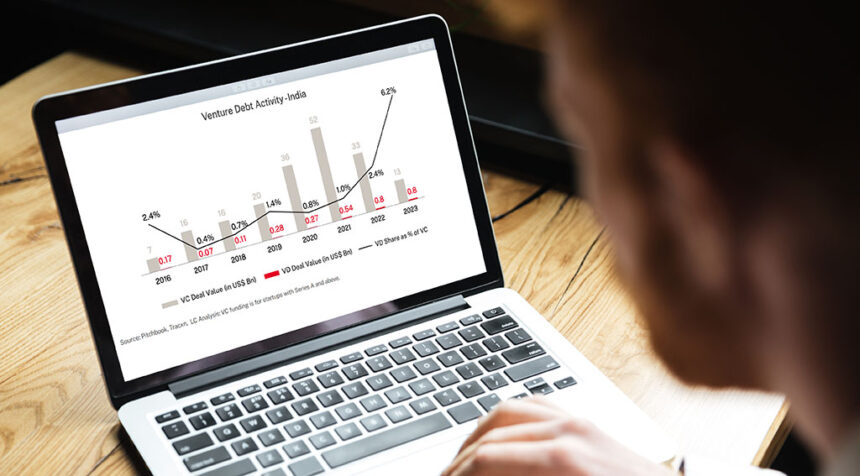
India’s VD market has been growing consistently over the past three years. VD’s total funding in 2020 was USD 270 million, only 0.8% of VC funding. By 2023, VD funding soared to USD 800 million, accounting for 6.2% of VC funding. This represents an increase of 675% between 2020 and 2023.

Despite this growth, India’s VD market is still in its infancy compared to more mature markets. In the US, VD has become a key component of the startup funding ecosystem, accounting for approximately 15-20% of total VC funding each year.

Featured image credit: Edited from freepic